In this post, we provide you with free, self-guided central Rome walking tours with a printable sightseeing map as well as an audio tour option for smartphones.
You can use these to discover the city at your own pace (or) as a preview for what you will see on a live-guided tour.
Check out our free walking tours of Rome.
We have 4 other self-guided tours that we hope you will consider.
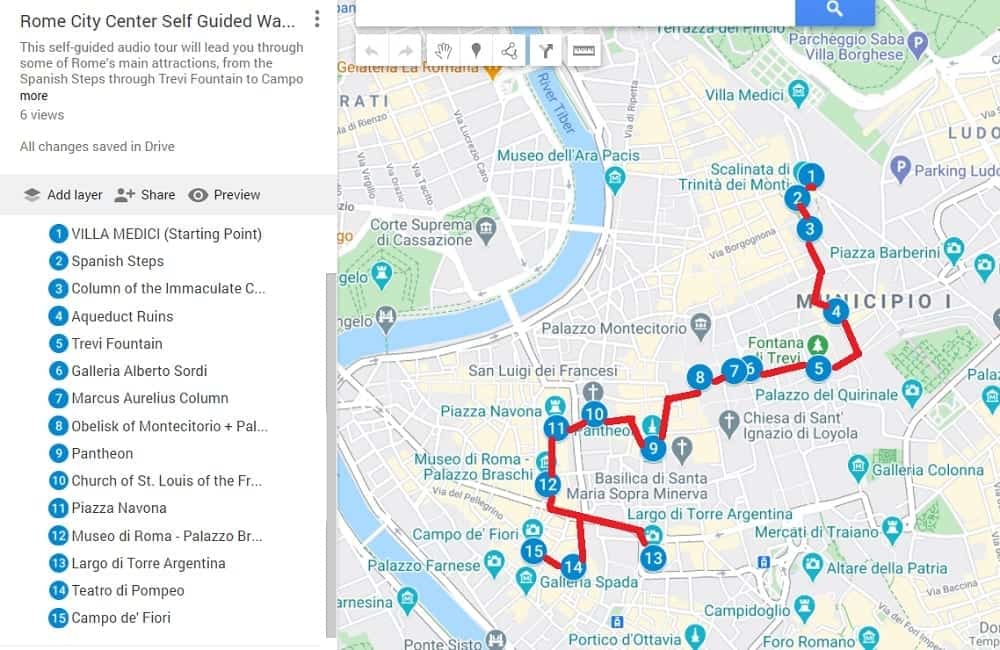
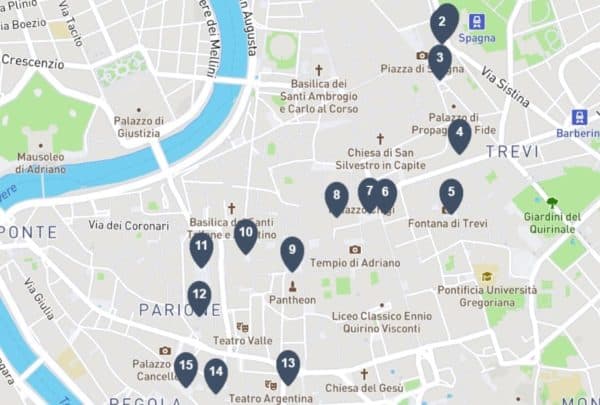
SELF-GUIDED TOUR OF ROME'S CENTRE
This self-guided tour will lead you through some of Rome’s main attractions, from the Spanish Steps through Trevi Fountain to Campo de’ Fiori.
All in all, there are lots of sights along the way covering more than two thousand years of history.
Here are a few of the sites you can expect to see on this tour:
- Piazza Navona
- The Pantheon
- Trevi Fountain
- Spanish Steps
- Venice Square
- Campo de’ Fiori

We also have our own audio tour where you can find a more in-depth GPS-led audio tour version. Here's a sample.
There are also daily guided free tours both day and night that really operate on the pay-what-you-like model.
Tours listed below are run through us. More guided tours are available here.
Searching Availability...
INTRO
This 15-stop, self-guided tour will lead you through some of Rome’s main attractions, from the Spanish Steps through Trevi Fountain to Campo de’ Fiori, with lots of sights along the way covering more than two thousand years of history.
It’s best to set aside 2-3 hours for walking this route.
You’ll be seeing plenty of both tourists and Romans as you walk, and both groups make good people-watching, not to mention plenty of chances for photos, coffee, gelato, and historical color.
Click on the map to enlarge or download it to a smartphone.
If you haven’t done much walking in the older parts of Rome yet, the ancient layout of these streets can be confusing.
Streets are winding, pedestrians and cars often share space, and you’ll regularly find your way into piazzas, the large open squares Rome is organized around.
You can get this tour with directions in 3 ways:
- Download this tour to the Google Maps App (link).
- Download a PDF version.
- Purchase an Audio Tour
We will be orienting you relative to buildings and with the help of street names, which you’ll see on signs up above eye level.
As far as timing, this tour can be enjoyed any time the sun is up, and some of the piazzas are lively even after dark.
Crowds can be a limiting factor throughout this walk; if you want to start things off on a quiet note, the Spanish Steps, one of our first stops, tend to be at their quietest early in the morning, briefly during lunch, and around sunset.

The tour begins at the Spagna metro station.
As you emerge from the western side of the building, you can look to your right and get a full view of the Villa Medici, not far down the street.
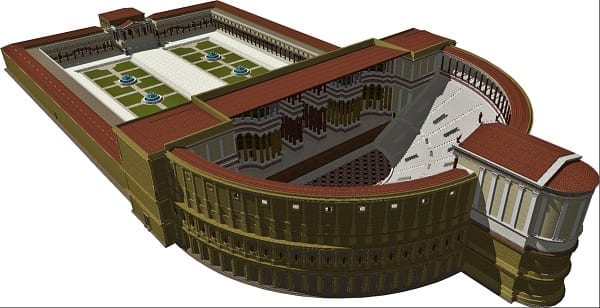
1. VILLA MEDICI
The Villa Medici, along with the Villa Borghese (which houses the Galleria Borghese) beyond it, stands on the site of the Gardens of Lucullus, created more than two thousand years ago, back when Romans saw gardening as a strange new hobby imported from Persia.
But the house you see today is built in 1576 after the land had been a quiet vineyard for centuries.
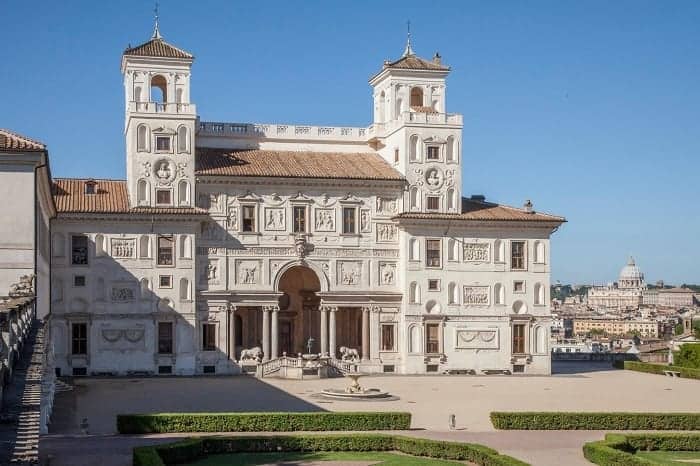

Villa Medici Rear
Houses like the Villa Medici were designed with ancient styles in mind, and inside, they often displayed the ancient relics found in the earth dug up to lay foundations.
The Medicis and Borgheses were some of Italy’s most powerful families during the Renaissance and beyond.
The Medici clan included bankers, nobility, and popes. But they’re remembered mostly for their support for the arts and sciences.
The Villa Medici offers guided tours daily, lasting about 90 minutes and available in different languages at different times.
It’s open every day but Monday and standard admission is 12 Euros.
Villa Borghese is home to the third-largest public park in Rome; admission is free and it’s accessible from dawn to dusk daily.
There are several things to see and do here in the park.
Most notably, it’s home to the Galleria Borghese, where you can see plenty of art and artifacts from both the Classical and Renaissance eras, plus several other museums and galleries.
The Villa Giulia contains a museum to the Etruscans, a rival culture of the early Romans.
In addition to the museums, there’s a zoo and a replica of Shakespeare’s Globe Theater on the grounds.
2. SPANISH STEPS
For many foreigners, the Spanish Steps are visual shorthand for Rome; they’re used in lots of movies and TV shows, starting with Roman Holiday back in 1953.
This was a natural hillside as recently as 1723. Before the steps were built, this was the slope of the Pincio Hill, one of many hills around Rome.
The 138 steps were built in the 18th century and got their name due to the adjacent Spanish Embassy.
Unfortunately as of 2019, you can no longer sit on the Spanish Steps. Violaters can receive a fine as high as €400.
Eating on the steps is also banned.
At the bottom of the steps sits the Piazza di Spagna and the Fontana della Barcaccia, which means “Fountain of the Long Boat.”
The legend goes that the design of the fountain comes from a boat washed into this piazza by a flood of the Tiber River.
This is the first of many fountains that we’ll see, and it’s designed by Pietro Bernini in the 17th century, before the steps.
Pietro Bernini is the father of famous architect Gian Lorenzo Bernini, whose work we’ll also see plenty of.
When you get to the bottom, look up the stairs for a view of that French church at the top, called Trinita dei Monti.
If you look to the right side of the steps from the bottom, you’ll see a peach-colored building, the Keats-Shelley Museum. English poet John Keats arrived to live here in 1820.
If a café stop is in order before you go any further, the Antico Caffe Greco near the bottom of the stairs was one of his hangouts.
When you’re done here, walk away from the steps and past the fountain. Turn left and you’ll see the piazza narrowing toward a freestanding column, the Column of the Immaculate Conception.
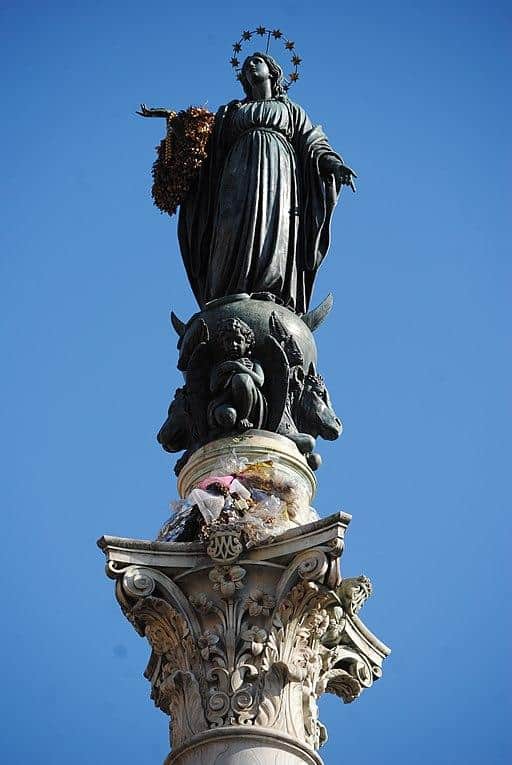
3. COLUMN OF THE IMMACULATE CONCEPTION AND PIAZZA MIGNANELLI
The Column of the Immaculate Conception is the centerpiece of the small Piazza Mignanelli that opens from the corner of the Piazza di Spagna.
The statue on top of the column is a bronze Virgin Mary. Mary, the mother of Jesus, occupies a central place in Catholic belief.
And this statue of her was built in 1857 to commemorate the Pope’s recent declaration of the Doctrine of the Immaculate Conception: the idea that Mary, uniquely among human beings, was born without original sin.
Original sin is visible in the monument in the form of the snake Mary is stepping on.
Below her are the authors of the four Biblical gospels, and still further down are four prophets said to have foretold her birth, with reliefs depicting four phases of her story below them.
Depending on when you’re here, there’s a small chance you’ll see a wreath of flowers on the statue.
December 8th is the Feast of the Immaculate Conception; each year on that day, the Pope visits this spot along with the head of the fire department, which originally erected the column, and they leave the wreath behind.
The building beyond the column is the Palazzo di Propaganda Fide – the Palace of the Propagation of the Faith.
This is a Vatican property – you can tell from the yellow flag on the front – and for a long time, it was the home of a church division responsible for missionary work and evangelism.
4. AQUEDUCT RUINS
Looking down at this spot, you can see something that an ancient Roman would have had to look up at.
The aqueducts – imperial Rome’s famous system for bringing clean water into the city – relied on gravity to work.
So, water was sometimes flowing over the heads of the people who were going to consume it, with roads passing under the arches you can see the top of from here.
Being by a river, Rome has flooded many times through the millennia, piling sediment each time, hiding but also preserving the ancient city.
The fence here limits the view, but above the arch, you can maybe see an inscription with the word “Germanicus” just readable at the near end.
This is one of the names of the emperor Claudius, who the inscription credits with rebuilding this stretch of the Aqua Virgo, the system of aqueducts built to bring water to the newly urbanizing Campus Martius after it was incorporated into the city.
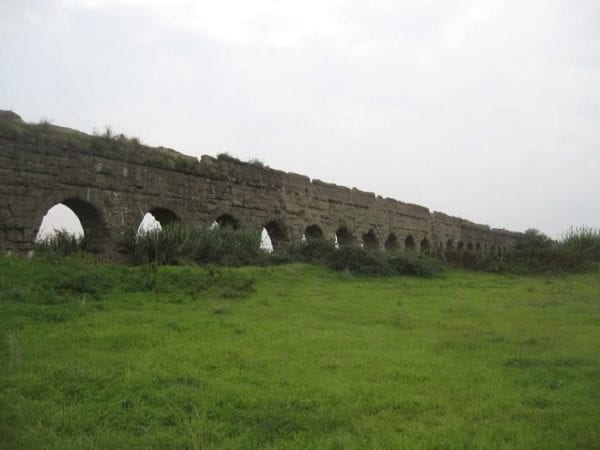

To achieve this, Roman engineers had to build a system of gentle slopes across long distances of irregular terrain, including crossing rivers, bringing convenience, comfort, and health within reach of Rome’s residents.
This knowledge was lost with the fall of Rome; with the Renaissance, writings about the aqueducts were rediscovered.
Across Via del Nazareno from these ruins is a tiny door, used to enter the rebuilt Acqua Vergine, the Renaissance replacement for the ancient system.
And in a moment, you’ll see another piece of that system: a fountain meant to put this reborn marvel of engineering on display.
5. TREVI FOUNTAIN
There’s likely to be a crowd around when you reach the Trevi Fountain, and even in the absence of people, the water can make it a loud spot. Find a view of the fountain from the front.

The main statue in the fountain depicts the god Oceanus. Below him, you can see his retinue of tritons, men mixed with fish.
The one on the right is blowing a shell to announce their arrival. And the wild creature each of them is struggling with is called a hippocampus, a horse mixed with a fish.
In this case, they also have wings. Greco-Roman mythology tells that horses were the creation of the god of the ocean.
The fountain is the end of the Acqua Vergine aqueduct, the recreation of the ancient Aqua Virgo aqueduct. And the design of the fountain tells that story.
Above the statues, on either side, you can see reliefs – the one on the left is a man with a scroll, showing plans for the aqueducts, and on the right, a woman points out a flow of freshwater to a group of men.
She’s the Virgo, the young woman, in Aqua Virgo – the legend is that when Roman surveyors looked for a source of water, a young woman led them to a spring, and the resulting aqueduct was named for her.
The statue on the left of Oceanus represents Abundance – she has a cornucopia full of fruit, and on the ground beside her is an urn spilling water.
On the right is Health, who’s holding a bowl with a snake drinking from it – snakes were ancient symbols of medicine.
Overall, the story is of the power of Rome to tame the forces of nature and bring them to the benefit of the city’s people.
As you see it, the fountain dates from 1762, and it started as a showpiece for the Renaissance project of rebuilding the aqueducts.
But it was such a massive endeavor that it took more than a century, plus many financiers and designers, to make it happen.
And it takes steady renovations to keep it looking sharp – as of the latest one in 2015, the fountain is lit at night.
Like the Spanish Steps, the Trevi Fountain owes some of its fame to a film – in this case, La Dolce Vita by Federico Fellini (see the video above).
If you’ve seen the movie, you won’t be surprised to hear that dancing in the fountain, or entering it in any way, is illegal.
And as for drinking: yes, these fountains were once the source for public drinking water, but for your own sake, wait for one of Rome’s other great works of water infrastructure, the nasoni – little drinking fountains located all over town.
Trevi Fountain is home to lots and lots of coins - visitors observe a tradition of throwing change into the fountain, hoping for good luck and the promise of a return to Rome.
Usually, coins are thrown backward over your shoulder, so make sure the coast is clear before you participate in this tradition, and watch out for other coin-tossers nearby.
And the money, totaling more than three thousand Euros per day, goes to Caritas Roma, a Catholic charity supporting the poor and homeless.
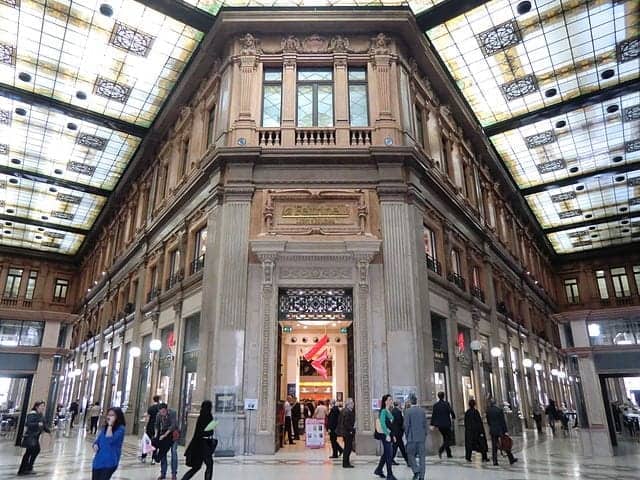
6. GALLERIA ALBERTO SORDI
All that’s columned is not ancient, as evidenced by this shopping mall, opened in 1922 and built in a style of Art Nouveau that borrows from multiple phases of Rome’s historic architecture.
That design continues into the inside, where you can find a stained glass ceiling above stores selling plenty of Rome’s signature high-end fashion.
It’s an easy place to step inside if you need to cool off or to use the restrooms.
You can also find several places serving the classic cappuccino and cornetto - Italian croissants, which locals eat in the morning, and tourists are allowed any time of day.
The mall got its current name in 2003 after the death of Alberto Sordi, a classic actor of Italian comedy films.
When you’re ready to move on, go back outside the way you came in and cross the street toward the Marcus Aurelius Column.
7. MARCUS AURELIUS COLUMN
The Marcus Aurelius column is much thicker than many similar monuments you’ll see around the city.
That’s because it’s hollow, with a spiral stairway inside that once allowed a climb to the top.
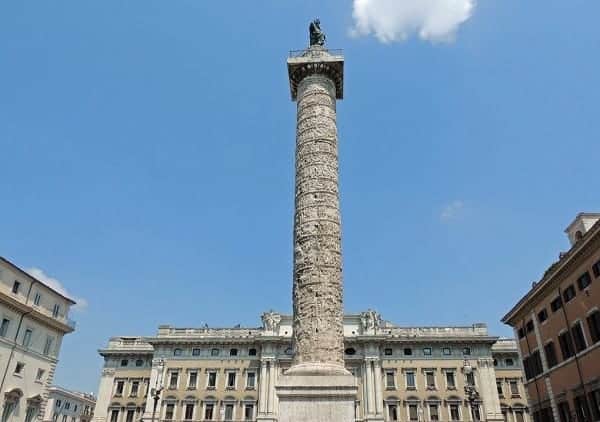

The spiral is also on the outside – you can see an unbelievably detailed relief up and down the length of the column. It shows battles led by Marcus Aurelius against the barbarians.
“Barbarian” is a broad term today, and it was broad for the Romans, too. These particular wars were against Germanic and Persian groups.
But the collective term “barbarian” could apply to almost any culture, and the word comes from “barbar,” meaning “blah blah” – so “barbarian” just meant “people who talk languages that don’t make sense.”
And the sculpture does not spare the details of the barbarian experience – towns are burning, women and children are running, and surviving soldiers are bent and horrified at the power of the empire.

The column was probably finished after Marcus Aurelius’ death, and at that time, it would have been the least of his honors in this area – near here stood the Temple of Marcus Aurelius.
After their deaths, most Roman emperors were declared gods and worshipped.
Nothing remains of that temple now, but temples to other Roman emperors do still remain.
Like all the ancient structures in the area, this column has been affected by floods and rising sediment, so several meters of it are below ground.
The statue on top is not Marcus Aurelius, but the Christian St. Paul, added when this monument received its own Renaissance restoration.
8. PALAZZO MONTECITORIO AND OBELISK OF MONTECITORIO
This obelisk is genuinely Egyptian, made in the 6th century BC and brought here five centuries later.
Earlier we mentioned that obelisks represented the divinity of Egyptian pharaohs.
The head of the Egyptian gods was Ra, the god of the sun, and this obelisk was used in Rome as part of an enormous sundial.
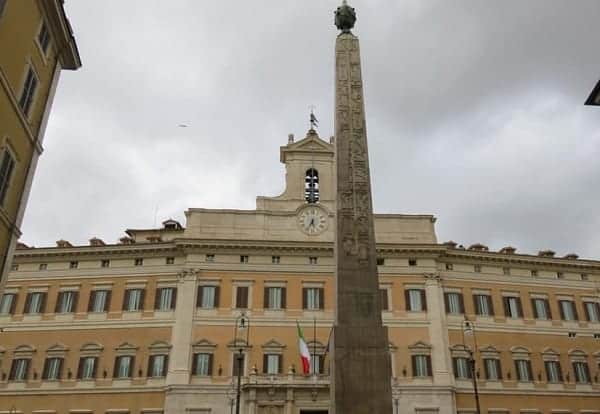

Like the others, it fell, was buried, and then was rediscovered, and like the others, it doesn’t stand at its original location
Today, there’s a meridian on the ground, pointing toward the piazza’s largest building, to nod at its former use.
The building that meridian points toward is the Palazzo Montecitorio. This palace is the home of the Chamber of Deputies, one of Italy’s two houses of Parliament.
Rome has been Italy’s capital since 1870, shortly after the Italian unification, when the many small, conflicting states in the region, separate since the fall of the Roman Empire, first joined into a single country.
The building itself, at least the part you can see, is much older – it’s another Renaissance creation.
And it’s originally the work of Gian Lorenzo Bernini, a Baroque architect, and sculptor we’ve mentioned, who also had a hand in the Trevi Fountain.
I also mentioned his father, who was another sculptor and who saw talent in Gian Lorenzo from a young age, giving him the benefit of early study and a long, prolific career.
Bernini’s sculptures are around the world, and his architecture is all over Rome.
He’s responsible for parts of St. Peter’s Basilica, the piazza outside of it, and a fountain in the Piazza Navona, which we’ll see soon, just to name a few.
This building shows the style he cultivated and which many others imitated, but if you got past the front door, everything you’d see is 20th-century Art Nouveau.
Apart from the façade, the building was completely remade to suit the needs of parliament.
9. PANTHEON
The name “Pantheon” is Greek, not Latin, meaning “for all the gods.”
The source of the name is uncertain – most temples were dedicated just to one god, not all of them together.
And there’s no record of how it was used in the 2nd century AD when it was finished under Emperor Hadrian.

And Hadrian was rebuilding an earlier temple, and the inscription above the entrance still dates from that nearly 2,000-year-old version.
You can still read the name of Agrippa, who ordered the original temple built.
You can also tell its age because it sits below the level of most of the ground around it, whereas originally it was elevated.
There are a couple of reasons why it’s lasted so long.
First, in the 7th century, when many ancient buildings were being abandoned or destroyed, the Pantheon became a Christian church, dedicated to St. Mary and the Martyrs; for a while it even had bell towers on the outside.
Even then, its refitting as a church meant the removal and destruction of many objects its new users considered unholy.
The other factor in its preservation is that the structure itself is built to last.
The dome on top is made of concrete, with thicker layers of heavier materials near the bottom, then gradually thinner and lighter going up.
It’s still the largest unreinforced concrete dome in the world.
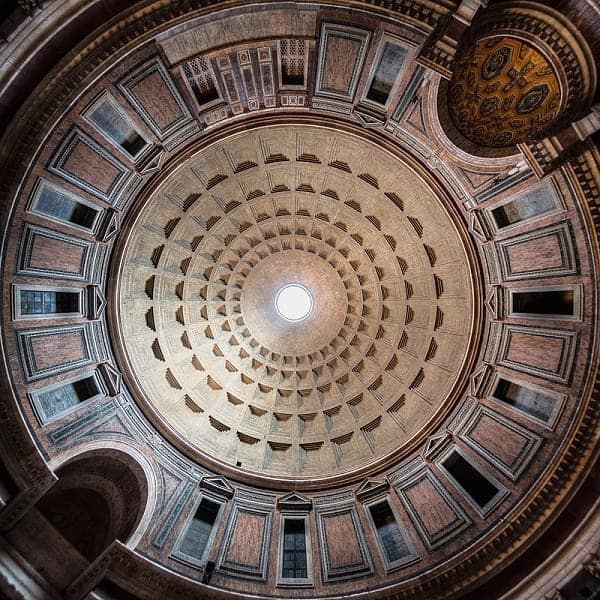

You can’t see it from outside, but at the very top of the dome is an opening, called the oculus or the eye.
Besides lightening the weight of the structure, it also means that from inside, you can see the sky and whatever the sky is doing.
Around noon, a dramatic beam of light becomes the centerpiece, assuming the sky is clear.
If the sky is not clear, then the weather comes in.
Standing inside during rain or snow can be magical (video), and also relatively peaceful since many visitors to town won’t want to make the trek to the Pantheon on foot during a storm.
If you go inside, you’ll see the altar, apses, and other markers of an active Catholic church.
Among the statues are markers of burial places, including the artist Raphael and the first two kings of unified Italy: Vittorio Emmanuele II and his son, Umberto I.
You can get lots more detail on the many features of the interior by taking a tour.
Live tours are plentiful, and just inside, you can get access to an official audio tour that’s affordable and detailed. There’s also an excellent free audio tour from Rick Steves.
If you just want to absorb the visuals, you can go in on your own. Regardless, you’re asked to keep silent while you’re inside.
It’s open Monday through Saturday, 8:30 am - 19:30 (7:30 pm), and Sunday 9:00 am - 18:00 (6 pm), and as of July 2020, it’s free to enter.
The Pantheon also hosts mass twice a week, at 17:00 (5 pm) on Saturday and 10:30 am on Sunday.
Outside the Pantheon is another obelisk, this one originally standing at a Temple of Ra in Heliopolis, Egypt, then at a temple to the Egyptian goddess Isis here in Rome, and then, finally, here in the Piazza della Rotonda.
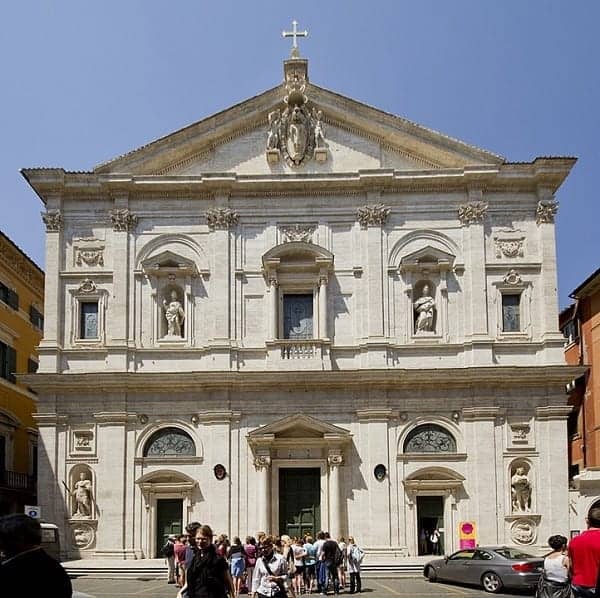
10. CHURCH OF ST. LOUIS OF THE FRENCH
The Church of San Luigi delle Francese is dedicated to several saints, but the name refers to Louis IX, the sainted king of France.
It’s another beneficiary of the Medici family’s donations and one of many cases of European powers creating and having an honorary connection to major buildings in Rome.
Among the many separate states that used to make up present-day Italy, there were the Papal States.
These were territories ruled by the pope in a non-religious capacity, on top of his role as a religious leader across the whole Catholic world.
Rome was the center of the Papal States, and today, it still contains the church’s political territory, Vatican City.
But when the Holy See was the main power here, churches like these represented a kind of embassy from other Catholic countries.
The church you see today dates from 1589, but it’s on a site used for the same purpose for possibly centuries before.
At ground level on the left, you can see a statue of Charlemagne, King of the Franks and Holy Roman Emperor.
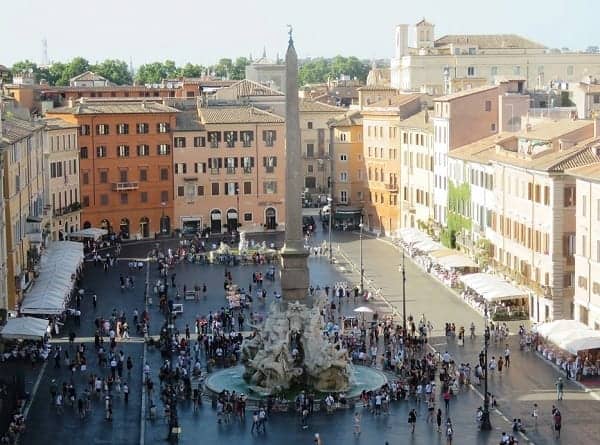
11. PIAZZA NAVONA
As you enter Piazza Navona, there are lots of possible first impressions, but I’ll suggest starting with the big picture.
You’ve seen piazzas in plenty of irregular shapes, but this one has the form of a long, narrow oval.
In the first century AD, this was a racecourse, part of the Stadium of Domitian, Rome’s first permanent stadium for athletic competitions.
If you go a block out of the piazza to the north – to your right – from the smaller Piazza di Tor Sanguigna, looking south, you can see some ruins of the stadium under a modern building. There is also a museum.
Besides those ruins, the oldest thing you can see is the Palazzo Pamphilj, the building on the opposite side from where you arrived on the far left.
This was the family home of 17th-century Pope Innocent X, and most of what you see in the piazza came from him improving his stomping grounds.
His work benefitted the general public in a way since this piazza was the city’s official public market.
But on the other hand, famines in that era meant that as these buildings were under construction, there wasn’t always food in those markets. Innocent’s home is now the Brazilian Embassy.
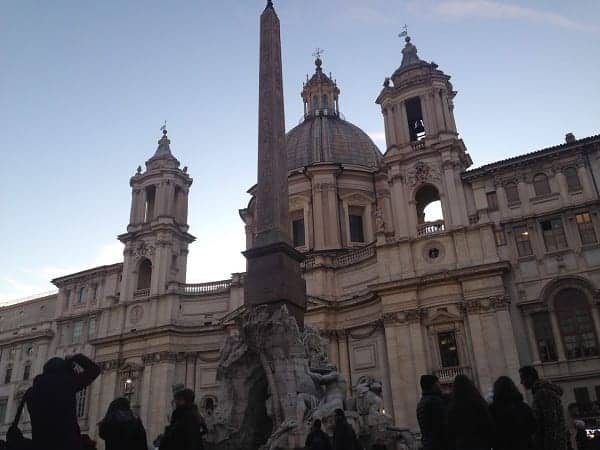

Sant’ Agnese in Agone (center) Palazzo Pamphilj (left)
He’s also responsible for the church to the right of his home, Sant’ Agnese in Agone. The Saint Agnes in the name of the church has a legendary connection with the Stadium of Domitian.
The Stadium contained brothels, and in the early years of Christianity, when the religion was still illegal in the Roman empire.
Agnes is said to have been punished for her religion by being sent there, only to have her hair miraculously grow to cover her body when she was stripped.
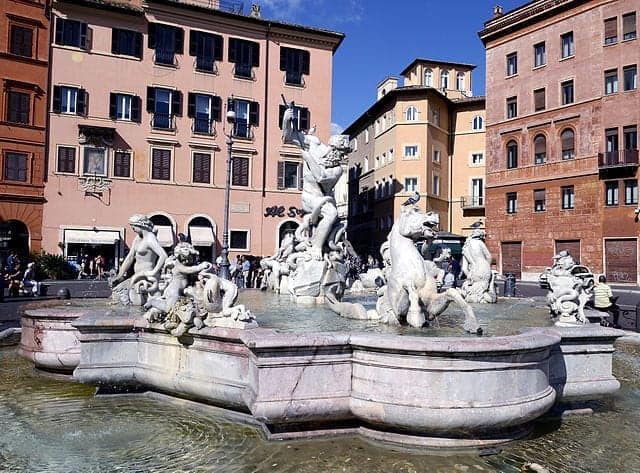

Fontana del Nettuno
The other famous feature of the Piazza Navona is its fountains.
At your right is the Fontana del Nettuno or the Fountain of Neptune, which shows the god of the ocean wrestling a sea monster, along with our old friend the hippocampus, and other water creatures.
The fountain itself is part of that 17th-century burst of improvements, but the statues are added much later.
On your left is the Fontana del Moro or Fountain of the Moor, added at the same time, again with later statuary.
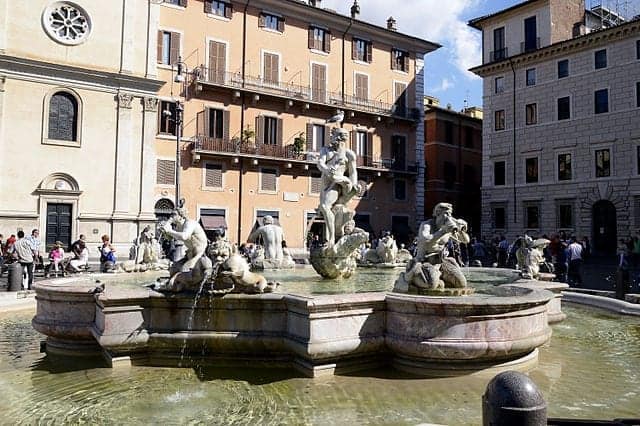

Fontana del Moro
And in the middle is the Fontana dei Quattro Fiumi or the Fountain of the Four Rivers. Here we’re in Bernini’s hands again, and we get to see him as both architect and sculptor.
The Four Rivers in the name are the four corners of the monument, each representing a river in what Romans of the 17th century considered the four parts of the world: the Danube in Europe, the Nile in Africa, the Ganges in Asia, and the Rio de la Plata in South America.
Italian explorers were very much in demand for expeditions to the New World, even if they sailed under other flags.
The details around each statue give a hint of which is which, and you can also see the expressiveness and sense of movement that Bernini’s sculptures are famous for.
All four are in submission, more or less willingly, to the obelisk at the center, which, like others we’ve seen, has a cross on top and so symbolizes the divine authority of the Church in Rome.
If you’d like a view of Piazza Navona from on high, the Brazilian Embassy has a rooftop bar that’s open to the public, and there’s also an optional view from our next stop.
When you’re ready, we’ll leave the piazza from the southern end, by the Fontana del Moro.
Once you have all three fountains behind you, turn right and leave the piazza on the Via di Pasquino, along the edge of the Brazilian Embassy.
When you reach an intersection, look on your left for a damaged statue behind a small chained barricade.

Pasquino
This is Pasquino, the namesake of the street. He’s older than any building you’ve seen, dug up and put on display in the 15th century.
He’s one of Rome’s “talking statues” – several places where it’s popular to post statements of protest, often in poetic form, and to get attention for your thoughts while remaining anonymous.
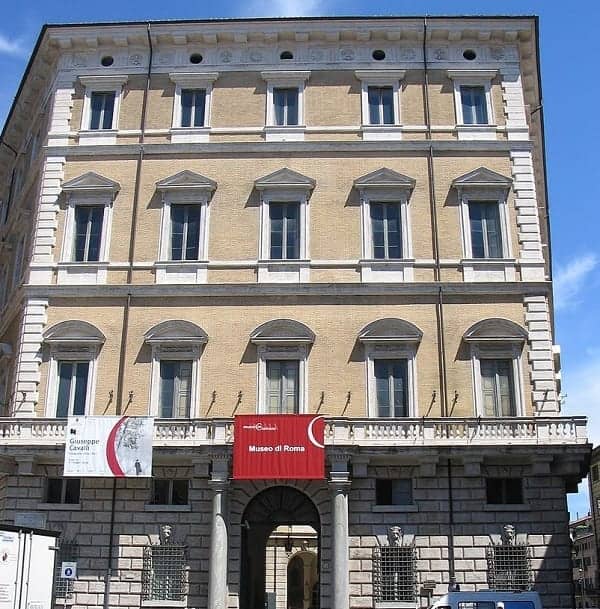
12. MUSEO DI ROMA – PALAZZO BRASCHI
The Palazzo Braschi was built as a home for the nephew of Pope Pius IX.
Along with the Piazza Navona, this was an example of popes exercising their political power to the benefit of their own family, and in this case, unlike the piazza, it was a purely private benefit.

Uses of power like this were part of what drove the wave of revolutions across Europe in the late 18th century and onward.
And that laid the groundwork for the Italian unification, which took some material power away from the popes. But the chance to abuse power fell into other hands.
In the early 20th century, this building was the headquarters of Benito Mussolini, the head of Italy’s fascist government.
During that time, the building had a massive image of Mussolini’s face on the side.
When that government fell after World War II, the city of Rome took over this property, and today it’s part of the Museum of Rome.
If you’re thinking about entering the museum, one of the attractions is a view over Piazza Navona from the second and third floors. You can also get a view of the piazza’s past from here.

The museum’s modest collection includes documentation of many bygone Roman scenes, including what Piazza Navona looked like before Pope Innocent, as well as what many historic sites looked like before a burst of demolitions in the early 20th century.
If your interest in Rome is at all to do with the layers of its history and how a modern city lives alongside the relics of its own past, this museum is worth your time, and the interior of the building itself is a beautiful bonus.
Information is available in English as well as Italian. It’s open 10:00 am - 19:00 (7 pm) every day but Monday and costs 11 Euros to enter.
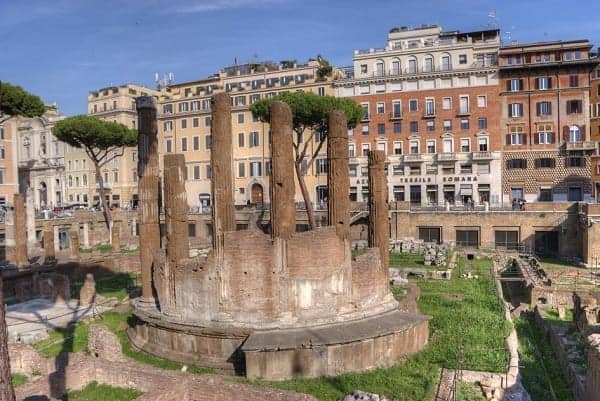
13. LARGO DI TORRE ARGENTINA
Innocuous as it is, this spot is one of the most read-about places in Rome, if not the most visited.
The ruins here include part of the Portico of Pompey, the place where Julius Caesar was stabbed to death in 44 BC.
Pompey, the building’s namesake, who you’ll hear more about soon, was Julius Caesar’s rival in a civil war, and after Caesar’s victory, Caesar was declared dictator.

Just a few years later, he was murdered, leading to a period of war that ended Rome’s time as a republic.
If you’re familiar with the story, you may remember that Julius Caesar was stabbed on the steps of the Senate.
At the time, the senate was temporarily meeting here, since the usual senate building was under a renovation that Caesar had ordered.
The spot was lost until 1929 when a demolition uncovered it. It also contains the remains of four temples, devoted to Roman gods that are less famous today.
But emperors and gods aside, people usually show up for the main attraction – cats!
As soon as the site was unearthed, a horde of homeless cats moved in, and today, it’s a shelter for mostly the injured and abused. Volunteers take care of feeding, healthcare, and spaying and neutering.
There’s a stairway that leads down into a gift shop and adoption area, where you can donate, meet volunteers, or hang out with the cats themselves.
14. THEATER OF POMPEY
You have to use your imagination for this part. Ancient Roman theaters were semicircular, with dozens of tiers of seats looking down toward a central half-circle stage.
An actor walking the lip of the stage could look at all the thousands of people in the theater in just a few steps.
Most theaters were temporary, but the first permanent one was the Theater of Pompey, and you’re walking the edge of its stage. That shape is the only remnant of the theater visible from here.
We mentioned Pompey at our last stop – his name was on the building where Julius Caesar was stabbed.
Pompey was a contemporary of Caesar’s, also a war hero to the Romans. After one of his victories, he announced he would build a theater for the public.
Theaters were popular but regarded as centers of vice, so permanent theater buildings were illegal within the city.
But Pompey built his in the Campus Martius, outside the city, and combined in a single facility a theater, a temple to Venus, a garden, and a sort of museum, with art representing great Roman works of the past and the many places Pompey had helped conquer for Rome.
So the place was also sort of a temple to Pompey himself. You’ll be able to see a tiny vestige from our next stop.
15. CAMPO DE’ FIORI
As you emerge into Campo de’ Fiori, look over your right shoulder at the short side of the piazza.
From the short buildings nearest to you, they get gradually taller to the left, and the walls meet at odd angles.
At one spot, you can see exposed, corroded brick – that’s a fragment of the Temple of Venus that once stood at the top of the Theater of Pompey.
The name Campo de’ Fiori is also ancient – before the theater was built, this area was a campo, meaning a field, of fiori, meaning flowers.
From there, we jump to the 16th century, which is the era of the shrouded figure you see standing on a pedestal halfway along the piazza.
That’s Giordano Bruno, a Dominican priest who was schooled in Naples, but became a wanderer of Europe after he found out the Inquisition was investigating him.
As a student, he had read forbidden works and argued unpopular positions, and his vagabond life sent him further down that road.
He claimed that the earth revolved around the sun, that the universe was infinite and contained many little systems like ours, and that everything big and small was made of tiny, similar particles arranged in different ways, with an invisible force holding them together – which in his eyes was God.
After years on the road, he returned home, and the Inquisition imprisoned him for seven years, tried him as a heretic, and burned him at the stake where the statue stands now.
The statue dates from soon after the unification and therefore secularization of Italy, and it was arranged by a group of Roman students, who sought out the help of a few famous writers in bringing attention to the cause.
They positioned it facing toward Vatican City. The inscription in Latin reads, “To Bruno, from the era he predicted, here where the fire burned.”
It’s still a rallying point for all kinds of nonconformist groups and causes today.
The beauty of an Italian piazza is that a story like that can be commemorated in the middle and a million other things are going on all around it.
Campo de’ Fiori is an eventful marketplace with cafes, restaurants, and people-watching galore. After all this exploring, maybe it’s time for those things, in which case you have lots of choices within view.